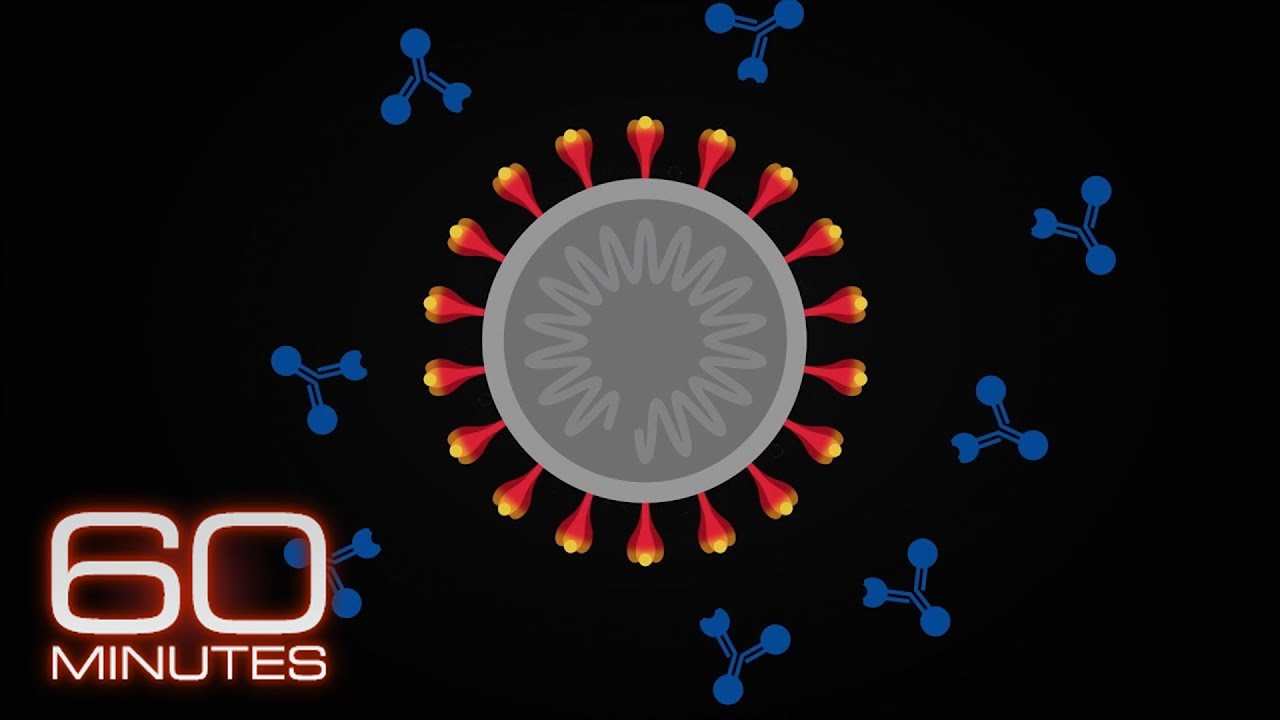
New, mutated strains of the coronavirus are causing worry around the world as health officials race to vaccinate as many people as possible. Dr. Jon LaPook reports on why the new strains are popping up.
“60 Minutes” is the most successful television broadcast in history. Offering hard-hitting investigative reports, interviews, feature segments and profiles of people in the news, the broadcast began in 1968 and is still a hit, over 50 seasons later, regularly making Nielsen’s Top 10.
Subscribe to the “60 Minutes” YouTube channel: http://bit.ly/1S7CLRu
Watch full episodes: http://cbsn.ws/1Qkjo1F
Get more “60 Minutes” from “60 Minutes: Overtime”: http://cbsn.ws/1KG3sdr
Follow “60 Minutes” on Instagram: http://bit.ly/23Xv8Ry
Like “60 Minutes” on Facebook: http://on.fb.me/1Xb1Dao
Follow “60 Minutes” on Twitter: http://bit.ly/1KxUsqX
Subscribe to our newsletter: http://cbsn.ws/1RqHw7T
Download the CBS News app: http://cbsn.ws/1Xb1WC8
Try Paramount+ free: https://bit.ly/2OiW1kZ
For licensing inquiries, contact: licensing@veritone.com
over 2 million americans are receiving
vaccinations every day fueling hope the end of the pandemic is near but since the sars
kovi 2 virus emerged in wuhan china 14 months ago over 100 million people worldwide have
been infected and with each infection the virus has had the chance to mutate into genetic
offspring called variants one of those variants first identified in the uk has spread across
the u.s and is estimated to be 50 percent more transmissible than the original virus and likely
more deadly nationwide covid19 cases have fallen but public health officials are warning
if these variants continue to spread they could trigger a new surge of infections
the story will continue in a moment news the uk variant had reached american
shores came last december at the university of california san diego you guys know the routine
the variant was found as part of an extensive coronavirus surveillance and testing system
that has kept nearly 25 thousand people living and working on campus thank you vending
machines designed to dispense candy bars now offer nasal swabs for covet testing and golf
carts go on daily runs collecting samples taken from wastewater oh there you go do you see it sure
so now if we pick this up environmental engineer smurfy kartikayan showed us how robots placed
near over 300 student dorms and research buildings suck up sewer samples looking for early evidence
someone might be infected with the virus and if there’s a positive what happens if there’s
a positive and they will send targeted notices saying you’re building the wastewater has
been positive and please go get tested many positive samples from wastewater and nasal
swabs are sent here to nearby scripps research where infectious disease researcher christian
anderson’s lab performs genetic sequencing to identify any variations it’s really important that
we keep an eye on the virus how is it evolving how is it transmitting how is it changing
genetic sequences from around the world are constantly being analyzed in a database called
neck strain that anderson and other scientists use to visualize how variants are spreading these
are beautiful colors but what am i looking at you can think of this as a family tree and what
we have is down here this is the first one in wuhan viruses mutate over time you see mutations
coming up and that’s when you start getting these branching patterns so then you have sisters and
brothers here and then you have ants and uncles and what’s the practical use of having a tree like
this the practical use is that somebody like me can go in and look at like how is this all related
since the original virus was first identified in december 2019 thousands of variants have been
documented anderson says scientists are keeping a close eye on three of them they call variance
of concern and that’s the uk variant which was you can see here was identified dates back to about
september of last year and then all of a sudden you get a lot of these and that’s because it’s
more transmissible so transmissible the centers for disease control has projected the uk variant
will be the dominant strain in the u.s in the next month the variants from brazil seen in red and
south africa seen in orange have already spread to dozens of countries including the u.s variants
arise because the sars-ko v2 virus is constantly making copies of itself as it replicates tiny
mistakes or mutations can occur in its genetic code they’re rare and usually insignificant but
once in a while one or more mutations team up to create a more dangerous variant of the
virus we are reading evolution’s lab notebook every time one of these pops up it’s telling us
exactly how evolution benefits at the expense of the fitness of humankind dr francis collins
director of the national institutes of health is a geneticist who 20 years ago oversaw the decoding
of the human genome he says he’s surprised by how much this virus is evolving why are the variants
of concern that we’re seeing in places like the united kingdom south africa and brazil of such
concern it turns out that some of these mutations actually change the behavior of this virus in
a way that makes it more infectious or more serious and the evidence is that for both the b117
which is primarily seen in the uk but increasingly in the us and the south africa and b1351 that
they are more transmissible they’re just really successful we’re seeing evolution in motion i
think it’s been rarely seen as clearly as right now how evolution works in that way it was pretty
predictable what wasn’t predictable for me anyway was that there would be so many copies of
this virus that even a slow evolutionary process could in just a matter of a few months
produce some viruses that we’re worried about and there’s so many copies because it’s a pandemic
and it’s been very successful in infecting millions and millions of people these samples
were from the patient’s lung an early clue about how the virus was mutating came last summer
at the university of pittsburgh medical center infectious disease specialist dr gotti haidar says
a cancer patient with a compromised immune system came in with a covid19 infection that persisted
for over 70 days far beyond the typical few weeks we had no idea at the time that people could
still be actively infectious for that long and it really wasn’t until after he passed away
that we started running some additional testing on samples that he had allowed us to
collect from him when he was alive and that’s when we found that the virus really
quickly began to develop all these deletions and mutations throughout the patient’s life
this electron microscope image shows a sample taken from the patient’s windpipe tiny spheres
looked like the original virus from wuhan china but genetic sequencing revealed a different story
there were small gaps where information should be irish-born university of pittsburgh
virologist paul dupre says the uk variant has some of these same deletions leading
some scientists to believe it may have started in an immunocompromised patient when you have
a patient who is sick for so long there’s the opportunity for the virus to replicate and
replicate and replicate and every time a virus has that opportunity to replicate there’s also
an opportunity for it to make a mistake right and that’s how viruses change those mistakes give
the virus just a little bit of a competitive edge for example kind of get into a cell better duprey
says yes he used this animation to show us how it starts with the spike protein seen in red
which the virus uses to latch onto and enter a human cell so if you’ve been infected you’ll
make antibodies these blue molecules that bind to the outside of the virus spike and what
they do is they block the virus getting into the cell they can’t bind the receptor now here’s
a variant the yellow illustrating the variant the antibodies can no longer bind the virus is able
to attach to that receptor latch on and bingo that person gets infected is there anything we
can do to stop the virus from mutating so much we can certainly stop it making as many
mutations by stopping it infecting as many people if we block its transmission if we wear a mask
if we get vaccinated if we do social distancing so there’s a practical thing that we can do
but physically biologically is there something that we can do is there a magic bullet that we
can shoot at it that stops at making mutations nope to understand the threat posed by mutations
public health experts are studying the brazilian city of manaus last spring kovitz swept through
the population leaving about 70 percent infected as a result some researchers believed the city had
reached herd immunity but then starting this past december epidemiologists suspect thousands
were re-infected with the brazilian variant hospitals there were overwhelmed health
officials reported up to 150 deaths a day and a recent study suggests the variant is more
infectious than earlier strains and may be better at evading antibodies we had a cluster of cases at
columbia university irving medical center dr david ho known for his groundbreaking hiv research is
now working to identify which variants are present in new york city since january his team has
analyzed over 2 000 nasal swabs taken from people who had tested positive for covid19 what
was unexpected was there were only sporadic cases the uk brazilian and south african variants but
instead we noticed that we had a homegrown variant something new something new that was dominating uh
and rising very rapidly how rapidly is it growing it’s over 20 percent over 20 percent so that’s
a rapid rise in the last couple of months dr ho says the new york city variant is doubling
roughly every two weeks and city health officials announced this past week they found the variant in
39 percent of the covet 19 samples they recently sequenced dr ho is concerned because that
variant shares a key mutation with one found in south africa several studies have looked at the
effectiveness of the three vaccines authorized in the u.s against that south african variant both in
laboratory tests and clinical trials the vaccines appear to be somewhat less effective at eliciting
an immune response or preventing infection but the companies anticipate the vaccines will
still provide protection from severe disease from that south african variant what people are worried
about is i got a vaccine i thought i was safe and now you’re talking about all these variants where
am i i’m in the same boat i got vaccinated and i felt protected for a while until we realized there
was so much of the homegrown varian in new york how do you put this in perspective for people who
are watching this right now i think we have to be a bit concerned but that doesn’t say the vaccines
don’t work even in south africa the vaccines still work to some extent it’s just not as highly
protective as we had against the original strain in addition vaccine may not protect against
infection but may protect against disease or death dr collins says so far the pfizer and modern
vaccines appear effective against the uk variant and this past week a small laboratory study
found the pfizer vaccine elicited the same strong immune response against the brazilian
variant as against the original virus drug companies say they are working to retool their
vaccines and create booster shots as needed to keep up with the variance what keeps you up at
night in terms of the variance down the line if i have an anxiety it’s something worse than the
south african variant is out there that will get to the point where the vaccines no longer appear
to be fully protective against a bad outcome and that will certainly drive us then to do
a redesign of the vaccines as quick as we can recently a variant has been found in new york
city that has some of the characteristics of the variant of concern found in south africa i’m
not on the surface of it overly alarmed about that but it’s going to deserve a real lab experiment
to make sure that our vaccines would still provide immunity against that there’s a ton of political
economic and other pressure to have these vaccines be successful is the government committed to being
totally transparent about these variants about whether or not the vaccines are working
or is there some kind of a filter there cannot be a filter i will not stand for
that neither will dr fauci and absolutely if we ever come across as having the truth of the
matter distorted by what is politically or economically convenient then we will have lost
the public trust dr collins says right now we have a window of opportunity a little poke in
your arm ready and that americans need to get vaccinated avoid large gatherings and wear
masks to prevent the virus from spreading and mutating even more to continue
to hear that this isn’t over yet has got to be a hard thing for all of us i don’t
want to sound so pessimistic though we are making amazing progress we just got to hang on and don’t
blow it at the end if you’re the guy running for the finish line don’t trip right there on the
10 yard line try to get all the way to the goal we we can see it we’re gonna get there but this
is not the moment to relax or stop running hard a year of covet 19 reporting when you
think that a year ago we said that as many as 20 people have died and now
it’s more than half a million at sixty minutesovertime.com