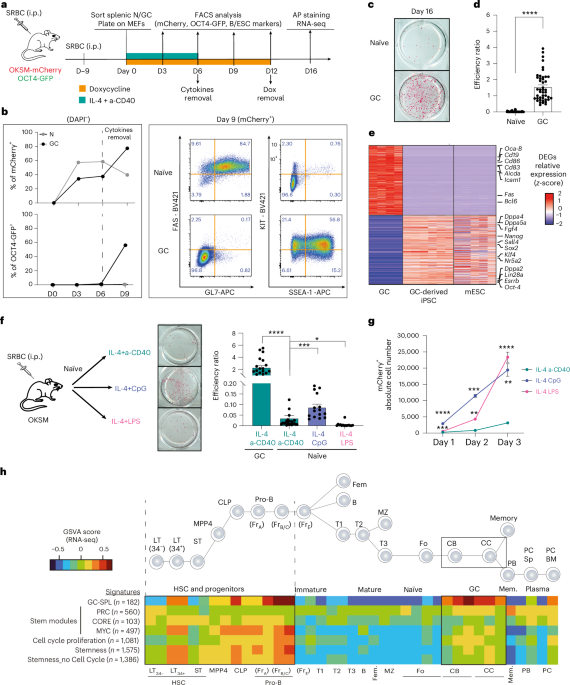
Mesin, L., Ersching, J. & Victora, G. D. Germinal center B cell dynamics. Immunity 45, 471–482 (2016).
Muramatsu, M. et al. Class switch recombination and hypermutation require activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potential RNA editing enzyme. Cell 102, 553–563 (2000).
Liu, M. et al. Two levels of protection for the B cell genome during somatic hypermutation. Nature 451, 841–845 (2008).
Pasqualucci, L. et al. Hypermutation of multiple proto-oncogenes in B-cell diffuse large-cell lymphomas. Nature 412, 341–346 (2001).
Shen, H. M., Peters, A., Baron, B., Zhu, X. & Storb, U. Mutation of BCL-6 gene in normal B cells by the process of somatic hypermutation of Ig genes. Science 280, 1750–1752 (1998).
Bal, E. et al. Super-enhancer hypermutation alters oncogene expression in B cell lymphoma. Nature 607, 808–815 (2022).
Ma, C. S., Deenick, E. K., Batten, M. & Tangye, S. G. The origins, function and regulation of T follicular helper cells. J. Exp. Med. 209, 1241–1253 (2012).
Suzuki, K., Grigorova, I., Phan, T. G., Kelly, L. M. & Cyster, J. G. Visualizing B cell capture of cognate antigen from follicular dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 206, 1485–1493 (2009).
Wang, X. et al. Follicular dendritic cells help establish follicle identity and promote B cell retention in germinal centers. J. Exp. Med. 208, 2497–2510 (2011).
Bannard, O. et al. Ubiquitin-mediated fluctuations in MHC class II facilitate efficient germinal center B cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 213, 993–1009 (2016).
Ise, W. et al. T follicular helper cell-germinal center B cell interaction strength regulates entry into plasma cell or recycling germinal center cell fate. Immunity 48, 702–715 e704 (2018).
Calado, D. P. et al. The cell-cycle regulator c-Myc is essential for the formation and maintenance of germinal centers. Nat. Immunol. 13, 1092–1100 (2012).
Dominguez-Sola, D. et al. The proto-oncogene MYC is required for selection in the germinal center and cyclic reentry. Nat. Immunol. 13, 1083–1091 (2012).
Ersching, J. et al. Germinal center selection and affinity maturation require dynamic regulation of mTORC1 kinase. Immunity 46, 1045–1058 e1046 (2017).
Pae, J. et al. Cyclin D3 drives inertial cell cycling in dark zone germinal center B cells. J. Exp. Med. 218, e20201699 (2021).
Victora, G. D. et al. Germinal center dynamics revealed by multiphoton microscopy with a photoactivatable fluorescent reporter. Cell 143, 592–605 (2010).
Gitlin, A. D. et al. T cell help controls the speed of the cell cycle in germinal center B cells. Science 349, 643–646 (2015).
Gitlin, A. D., Shulman, Z. & Nussenzweig, M. C. Clonal selection in the germinal centre by regulated proliferation and hypermutation. Nature 509, 637–640 (2014).
Dominguez, P. M. et al. TET2 deficiency causes germinal center hyperplasia, impairs plasma cell differentiation, and promotes B-cell lymphomagenesis. Cancer Discov. 8, 1632–1653 (2018).
Dominguez, P. M. et al. DNA methylation dynamics of germinal center B cells are mediated by AID. Cell Rep. 12, 2086–2098 (2015).
Rosikiewicz, W. et al. TET2 deficiency reprograms the germinal center B cell epigenome and silences genes linked to lymphomagenesis. Sci. Adv. 6, eaay5872 (2020).
Shaknovich, R. et al. DNA methyltransferase 1 and DNA methylation patterning contribute to germinal center B-cell differentiation. Blood 118, 3559–3569 (2011).
Ortega-Molina, A. et al. The histone lysine methyltransferase KMT2D sustains a gene expression program that represses B cell lymphoma development. Nat. Med. 21, 1199–1208 (2015).
Velichutina, I. et al. EZH2-mediated epigenetic silencing in germinal center B cells contributes to proliferation and lymphomagenesis. Blood 116, 5247–5255 (2010).
Beguelin, W. et al. EZH2 is required for germinal center formation and somatic EZH2 mutations promote lymphoid transformation. Cancer Cell 23, 677–692 (2013).
Hatzi, K. et al. Histone demethylase LSD1 is required for germinal center formation and BCL6-driven lymphomagenesis. Nat. Immunol. 20, 86–96 (2019).
Leung, W. et al. SETD2 haploinsufficiency enhances germinal center-associated AICDA somatic hypermutation to drive B-cell lymphomagenesis. Cancer Discov. 12, 1782–1803 (2022).
Li, J. et al. Loss of CREBBP and KMT2D cooperate to accelerate lymphomagenesis and shape the lymphoma immune microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 15, 2879 (2024).
Barisic, D. et al. ARID1A orchestrates SWI/SNF-mediated sequential binding of transcription factors with ARID1A loss driving pre-memory B cell fate and lymphomagenesis. Cancer Cell 42, 583–604 e511 (2024).
Doane, A. S. et al. OCT2 pre-positioning facilitates cell fate transition and chromatin architecture changes in humoral immunity. Nat. Immunol. 22, 1327–1340 (2021).
Bunting, K. L. et al. Multi-tiered reorganization of the genome during B cell affinity maturation anchored by a germinal center-specific locus control region. Immunity 45, 497–512 (2016).
Chu, C. S. et al. Unique immune cell coactivators specify locus control region function and cell stage. Mol. Cell 80, 845–861 e810 (2020).
Vilarrasa-Blasi, R. et al. Dynamics of genome architecture and chromatin function during human B cell differentiation and neoplastic transformation. Nat. Commun. 12, 651 (2021).
Gorelov, R. & Hochedlinger, K. A cellular identity crisis? Plasticity changes during aging and rejuvenation. Genes Dev. 38, 823–842 (2024).
Tata, P. R. & Rajagopal, J. Cellular plasticity: 1712 to the present day. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 43, 46–54 (2016).
Waddington, C. H. The Strategy of the Genes (Routledge, 2014).
Stadtfeld, M. & Hochedlinger, K. Induced pluripotency: history, mechanisms and applications. Genes Dev. 24, 2239–2263 (2010).
Takahashi, K. & Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676 (2006).
Di Stefano, B. et al. C/EBPalpha poises B cells for rapid reprogramming into induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 506, 235–239 (2014).
Eminli, S. et al. Differentiation stage determines potential of hematopoietic cells for reprogramming into induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Genet. 41, 968–976 (2009).
Hanna, J. et al. Direct cell reprogramming is a stochastic process amenable to acceleration. Nature 462, 595–601 (2009).
Bar-Nur, O., Russ, H. A., Efrat, S. & Benvenisty, N. Epigenetic memory and preferential lineage-specific differentiation in induced pluripotent stem cells derived from human pancreatic islet beta cells. Cell Stem Cell 9, 17–23 (2011).
Kim, K. et al. Epigenetic memory in induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 467, 285–290 (2010).
Ohi, Y. et al. Incomplete DNA methylation underlies a transcriptional memory of somatic cells in human iPS cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 13, 541–549 (2011).
Polo, J. M. et al. A molecular roadmap of reprogramming somatic cells into iPS cells. Cell 151, 1617–1632 (2012).
Schmidt, R. & Plath, K. The roles of the reprogramming factors Oct4, Sox2 and Klf4 in resetting the somatic cell epigenome during induced pluripotent stem cell generation. Genome Biol. 13, 251 (2012).
Vierbuchen, T. & Wernig, M. Molecular roadblocks for cellular reprogramming. Mol. Cell 47, 827–838 (2012).
Apostolou, E. & Hochedlinger, K. Chromatin dynamics during cellular reprogramming. Nature 502, 462–471 (2013).
Huyghe, A. et al. Comparative roadmaps of reprogramming and oncogenic transformation identify Bcl11b and Atoh8 as broad regulators of cellular plasticity. Nat. Cell Biol. 24, 1350–1363 (2022).
Stadtfeld, M., Maherali, N., Borkent, M. & Hochedlinger, K. A reprogrammable mouse strain from gene-targeted embryonic stem cells. Nat. Methods 7, 53–55 (2010).
Bar-Nur, O. et al. Small molecules facilitate rapid and synchronous iPSC generation. Nat. Methods 11, 1170–1176 (2014).
Lengner, C. J. et al. Oct4 expression is not required for mouse somatic stem cell self-renewal. Cell Stem Cell 1, 403–415 (2007).
Wernig, M. et al. In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. Nature 448, 318–324 (2007).
Polo, J. M. et al. Cell type of origin influences the molecular and functional properties of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 28, 848–855 (2010).
Di Giammartino, D. C. et al. KLF4 is involved in the organization and regulation of pluripotency-associated three-dimensional enhancer networks. Nat. Cell Biol. 21, 1179–1190 (2019).
Gaspar, J. A. et al. Gene expression signatures defining fundamental biological processes in pluripotent, early and late differentiated embryonic stem cells. Stem. Cells Dev. 21, 2471–2484 (2012).
Glover, C. H. et al. Meta-analysis of differentiating mouse embryonic stem cell gene expression kinetics reveals early change of a small gene set. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2, e158 (2006).
Ivanova, N. B. et al. A stem cell molecular signature. Science 298, 601–604 (2002).
Mikkelsen, T. S. et al. Dissecting direct reprogramming through integrative genomic analysis. Nature 454, 49–55 (2008).
Ramalho-Santos, M., Yoon, S., Matsuzaki, Y., Mulligan, R. C. & Melton, D. A. ‘Stemness’: transcriptional profiling of embryonic and adult stem cells. Science 298, 597–600 (2002).
Wong, D. J. et al. Module map of stem cell genes guides creation of epithelial cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2, 333–344 (2008).
Yoshida, H. et al. The cis-regulatory atlas of the mouse immune system. Cell 176, 897–912 e820 (2019).
Kim, J. et al. A Myc network accounts for similarities between embryonic stem and cancer cell transcription programs. Cell 143, 313–324 (2010).
Beguelin, W. et al. Mutant EZH2 induces a pre-malignant lymphoma niche by reprogramming the immune response. Cancer Cell 37, 655–673 e611 (2020).
Rivas, M. A. et al. Cohesin core complex gene dosage contributes to germinal center derived lymphoma phenotypes and outcomes. Front. Immunol. 12, 688493 (2021).
Yusufova, N. et al. Histone H1 loss drives lymphoma by disrupting 3D chromatin architecture. Nature 589, 299–305 (2021).
Victora, G. D. & Nussenzweig, M. C. Germinal centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 40, 413–442 (2022).
Francesconi, M. et al. Single cell RNA-seq identifies the origins of heterogeneity in efficient cell transdifferentiation and reprogramming. Elife 8, e41627 (2019).
Morin, R. D. et al. Somatic mutations altering EZH2 (Tyr641) in follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of germinal-center origin. Nat. Genet. 42, 181–185 (2010).
Beguelin, W. et al. EZH2 and BCL6 cooperate to assemble CBX8-BCOR complex to repress bivalent promoters, mediate germinal center formation and lymphomagenesis. Cancer Cell 30, 197–213 (2016).
Mlynarczyk, C. et al. BTG1 mutation yields supercompetitive B cells primed for malignant transformation. Science 379, eabj7412 (2023).
Granja, J. M. et al. ArchR is a scalable software package for integrative single-cell chromatin accessibility analysis. Nat. Genet. 53, 403–411 (2021).
Guo, M. et al. A monoclonal antibody to the DEC-205 endocytosis receptor on human dendritic cells. Hum. Immunol. 61, 729–738 (2000).
Victora, G. D. et al. Identification of human germinal center light and dark zone cells and their relationship to human B-cell lymphomas. Blood 120, 2240–2248 (2012).
Cobaleda, C., Schebesta, A., Delogu, A. & Busslinger, M. Pax5: the guardian of B cell identity and function. Nat. Immunol. 8, 463–470 (2007).
Dominguez-Sola, D. et al. The FOXO1 transcription factor instructs the germinal center dark zone program. Immunity 43, 1064–1074 (2015).
Inoue, T. et al. The transcription factor Foxo1 controls germinal center B cell proliferation in response to T cell help. J. Exp. Med. 214, 1181–1198 (2017).
Sander, S. et al. PI3 Kinase and FOXO1 transcription factor activity differentially control B cells in the germinal center light and dark zones. Immunity 43, 1075–1086 (2015).
Whyte, W. A. et al. Master transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key cell identity genes. Cell 153, 307–319 (2013).
Grosveld, F., van Staalduinen, J. & Stadhouders, R. Transcriptional regulation by (super)enhancers: from discovery to mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 22, 127–146 (2021).
Schep, A. N., Wu, B., Buenrostro, J. D. & Greenleaf, W. J. chromVAR: inferring transcription-factor-associated accessibility from single-cell epigenomic data. Nat. Methods 14, 975–978 (2017).
Koike, T., Harada, K., Horiuchi, S. & Kitamura, D. The quantity of CD40 signaling determines the differentiation of B cells into functionally distinct memory cell subsets. eLife 8, e44245 (2019).
Jang, J. Y. et al. A FOXO1-dependent transcription network is a targetable vulnerability of mantle cell lymphomas. J. Clin. Invest. 132, e160767 (2022).
Langlet, F. et al. Selective inhibition of FOXO1 activator/repressor balance modulates hepatic glucose handling. Cell 171, 824–835 e818 (2017).
Willcockson, M. A. et al. H1 histones control the epigenetic landscape by local chromatin compaction. Nature 589, 293–298 (2021).
Fan, Y. et al. H1 linker histones are essential for mouse development and affect nucleosome spacing in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 4559–4572 (2003).
Perez-Gonzalez, A., Bevant, K. & Blanpain, C. Cancer cell plasticity during tumor progression, metastasis and response to therapy. Nat. Cancer 4, 1063–1082 (2023).
Donati, G. & Amati, B. MYC and therapy resistance in cancer: risks and opportunities. Mol. Oncol. 16, 3828–3854 (2022).
Jakobsen, S. T. et al. MYC activity at enhancers drives prognostic transcriptional programs through an epigenetic switch. Nat. Genet. 56, 663–674 (2024).
Petrich, A. M., Nabhan, C. & Smith, S. M. MYC-associated and double-hit lymphomas: a review of pathobiology, prognosis, and therapeutic approaches. Cancer 120, 3884–3895 (2014).
Agirre, X. et al. Long non-coding RNAs discriminate the stages and gene regulatory states of human humoral immune response. Nat. Commun. 10, 821 (2019).
Ennishi, D. et al. TMEM30A loss-of-function mutations drive lymphomagenesis and confer therapeutically exploitable vulnerability in B-cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 26, 577–588 (2020).
Reddy, A. et al. Genetic and functional drivers of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cell 171, 481–494 e415 (2017).
Schmitz, R. et al. Genetics and pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 378, 1396–1407 (2018).
Alizadeh, A. A. et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403, 503–511 (2000).
Wright, G. W. et al. A probabilistic classification tool for genetic subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma with therapeutic implications. Cancer Cell 37, 551–568 e514 (2020).
DuPage, M. & Bluestone, J. A. Harnessing the plasticity of CD4+ T cells to treat immune-mediated disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 149–163 (2016).
Sica, A. & Mantovani, A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J. Clin. Invest. 122, 787–795 (2012).
Ge, Y. & Fuchs, E. Stretching the limits: from homeostasis to stem cell plasticity in wound healing and cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 19, 311–325 (2018).
Flavahan, W. A., Gaskell, E. & Bernstein, B. E. Epigenetic plasticity and the hallmarks of cancer. Science 357, eaal2380 (2017).
Pitarresi, J. R. & Stanger, B. Z. Cellular origins and lineage plasticity in cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a041389 (2023).
Yuan, S., Norgard, R. J. & Stanger, B. Z. Cellular plasticity in cancer. Cancer Discov. 9, 837–851 (2019).
Herrera, E., Martinez, A. C. & Blasco, M. A. Impaired germinal center reaction in mice with short telomeres. EMBO J. 19, 472–481 (2000).
Hu, B. T., Lee, S. C., Marin, E., Ryan, D. H. & Insel, R. A. Telomerase is up-regulated in human germinal center B cells in vivo and can be re-expressed in memory B cells activated in vitro. J. Immunol. 159, 1068–1071 (1997).
Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 12, 31–46 (2022).
Hanahan, D. & Weinberg, R. A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011).
Guldenpfennig, C., Teixeiro, E. & Daniels, M. NF-kB’s contribution to B cell fate decisions. Front. Immunol. 14, 1214095 (2023).
Pelzer, C. & Thome, M. IKKα takes control of canonical NF-kB activation. Nat. Immunol. 12, 815–816 (2011).
Cao, Y., Yi, Y., Han, C. & Shi, B. NF-kB signaling pathway in tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 15, 1476030 (2024).
Jiang, C. et al. Innate immunity and the NF-κB pathway control prostate stem cell plasticity, reprogramming and tumor initiation. Nat. Cancer 6, 1537–1558 (2025).
Sardina, J. L. et al. Transcription factors drive Tet2-mediated enhancer demethylation to reprogram cell fate. Cell Stem Cell 23, 905–906 (2018).
Boller, S. et al. Pioneering activity of the C-terminal domain of EBF1 shapes the chromatin landscape for B cell programming. Immunity 44, 527–541 (2016).
Apostolou, E. & Stadtfeld, M. Cellular trajectories and molecular mechanisms of iPSC reprogramming. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 52, 77–85 (2018).
Cyster, J. G. Germinal centers: gaining strength from the dark side. Immunity 43, 1026–1028 (2015).
Rais, Y. et al. Deterministic direct reprogramming of somatic cells to pluripotency. Nature 502, 65–70 (2013).
Esteller, M. et al. The epigenetic hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Discov. 14, 1783–1809 (2024).
Loh, J. J. & Ma, S. Hallmarks of cancer stemness. Cell Stem Cell 31, 617–639 (2024).
Weinberg, O. K. & Arber, D. A. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: historical overview and a new definition. Leukemia 24, 1844–1851 (2010).
Chang, K. C. et al. Stem cell characteristics promote aggressiveness of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 10, 21342 (2020).
Martinez-Climent, J. A., Fontan, L., Gascoyne, R. D., Siebert, R. & Prosper, F. Lymphoma stem cells: enough evidence to support their existence? Haematologica 95, 293–302 (2010).
Mlynarczyk, C., Fontan, L. & Melnick, A. Germinal center-derived lymphomas: the darkest side of humoral immunity. Immunol. Rev. 288, 214–239 (2019).
Hu, F. et al. Degree of stemness predicts micro-environmental response and clinical outcomes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and identifies a potential targeted therapy. Front. Immunol. 13, 1012242 (2022).
in Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health (National Academies Press, 2011).
Xia, M. et al. BCL10 mutations define distinct dependencies guiding precision therapy for DLBCL. Cancer Discov. 12, 1922–1941 (2022).
Craig, R. et al. IL-1β stimulates a novel axis within the NFkB pathway in endothelial cells regulated by IKKα and TAK-1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 232, 116736 (2025).
Riley, C. et al. Design and synthesis of novel aminoindazole-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine inhibitors of IKKα that selectively perturb cellular non-canonical NF-kB signalling. Molecules https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29153515 (2024).
Hao, Y. et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 184, 3573–3587 e3529 (2021).
Dobin, A. et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29, 15–21 (2013).
Liao, Y., Smyth, G. K. & Shi, W. The R package Rsubread is easier, faster, cheaper and better for alignment and quantification of RNA sequencing reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, e47 (2019).
Subramanian, A. et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15545–15550 (2005).
Hanzelmann, S., Castelo, R. & Guinney, J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics 14, 7 (2013).
Pelham-Webb, B. et al. H3K27ac bookmarking promotes rapid post-mitotic activation of the pluripotent stem cell program without impacting 3D chromatin reorganization. Mol. Cell 81, 1732–1748 e1738 (2021).