Many people are aware of making sure they have enough vitamin C or D but there is one which is less thought of but that can still have serious health implications
13:34, 31 Dec 2025Updated 14:15, 31 Dec 2025
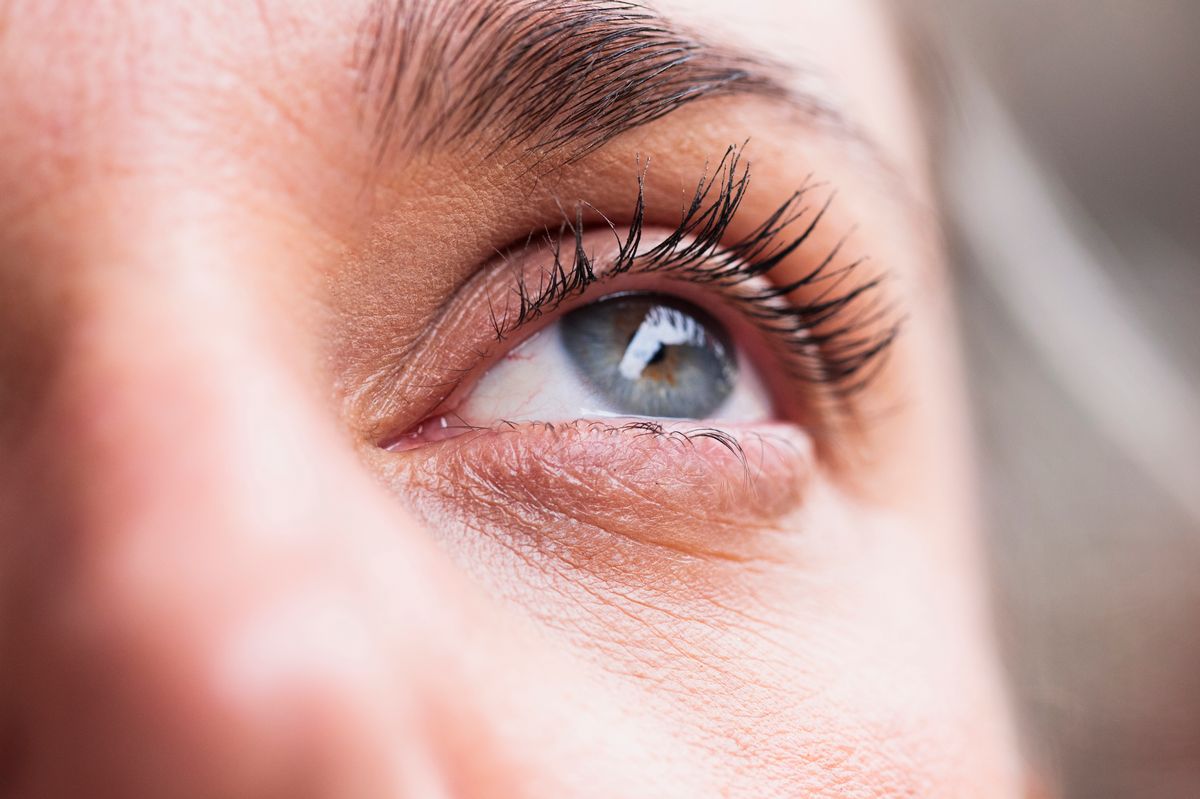 A deficiency can affect your vision(Image: Getty)
A deficiency can affect your vision(Image: Getty)
Many people will keep an eye on their intake of vitamins and minerals to ensure they stay fit and well. And when doubts creep in, it can mean extra attention, such as eating more oranges to boost vitamin C or adding spinach to salads to increase iron and calcium levels.
But one vitamin is rarely considered, despite it having a risk of severe health problems if it drops too low. Vitamin E is vital for a healthy immune system. An insufficient level means your body cannot function correctly.
Most people get all they need from a healthy diet, which means it is rarely thought about. However, those with some conditions, which mean their body does not absorb fat properly, can find they are not getting all the nutrients they need from their diet.
According to the Cleveland Clinic vitamin E is an antioxidant. This protects your cells from free radicals.
It says: “Free radicals are chemical reactions that can damage your cells. Your body needs plenty of vitamin E to fight free radicals. If you lack vitamin E, your immune system may have trouble protecting you against illnesses and infections.”
It says the vitamin is also important because it:
Supports healthy skinPromotes good visionPrevents blood clotsReduces inflammationSigns of Vitamin E deficiency
“Vitamin E deficiency symptoms mostly affect your nervous system,” warns The Cleveland Clinic. “These may include muscle weakness, vision issues and problems controlling your body movements.
“Other symptoms include numbness and fatigue. Severe cases can lead to blindness.” Further symptoms of vitamin E deficiency can include:
Bleeding within the brainAbnormal growth of blood vessels in the eyesA blood disorder called hemolytic anaemiaSlow reflexesTrouble walkingWeakened immune systemCauses of vitamin E deficiency
The Cleveland Clinic explains: “Fat absorption disorders and certain genetic disorders usually cause vitamin E deficiency. Less commonly, low vitamin E intake causes the condition. Vitamin E is found in many foods. So people who are healthy rarely have the deficiency.”
Fat absorption disorders
In countries such as the UK and USA where there is usually plenty of food for most people, vitamin E deficiency is uncommon. If you do have vitamin E deficiency, it’s often due to a disorder that prevents your body from absorbing fat. These diseases include:
Liver diseasePancreatitisCystic fibrosisCrohn’s diseaseCeliac disease
Certain rare genetic diseases can also lead to the condition. These include abetalipoproteinemia and ataxia with vitamin E deficiency.
Low intake of vitamin E
In countries with high rates of food insecurity, the most common cause of vitamin E deficiency is a lack of vitamin E in the foods you eat. A very low-fat diet doesn’t contain a lot of vitamin E. And your body needs some fat to digest and absorb it.
Those most at risk?
The Cleveland Clinic says: “Newborns — particularly premature infants — have a higher risk of being deficient in vitamin E. That’s because very little vitamin E crosses the placenta during fetal development. So, when they’re born, they don’t have a lot of the vitamin stocked up.
“With age, their risk goes down. Babies can usually get the vitamin E they need through breast milk or formula. Your risk of developing vitamin E deficiency goes up if you don’t eat foods with any fat in them. Your body needs fat to digest and absorb certain vitamins.”
When to see a doctor
If you have any of these symptoms, the Cleveland Clinic recommends you contact your healthcare provider