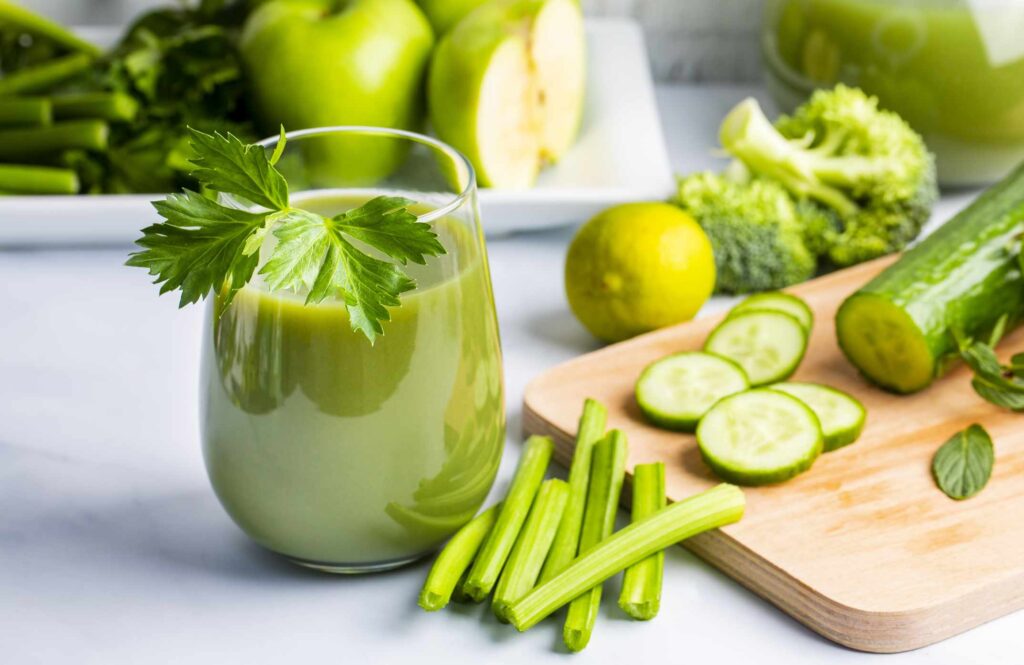
Green juice is made from blended green vegetables like spinach, kale, celery, and cucumber. The ingredients provide a rich source of vitamins and minerals, delivering a boost of hydration and nourishment.
Green vegetables contain vitamins A, C, E, and K. These nutrients support your immune system, skin health, and bone strength. They’re also a good source of minerals like iron, calcium, and magnesium, which support energy and muscle function.
Leafy greens like spinach and kale are particularly nutrient-dense. One benefit of juicing is that it concentrates these nutrients into a smaller serving, making it easier to consume more than you might typically eat in one sitting.
Vegetables like cabbage, celery, spinach, and lettuce are over 90% water. These ingredients make green juice an excellent source of fluids, helping you stay hydrated.
You get roughly 20% of your water intake from the food you eat. Drinking vegetable-rich green juice contributes to your hydration needs while providing essential nutrients.
Green vegetables contain plant compounds called polyphenols and flavonoids. These compounds have antioxidant properties that help protect cells from damage caused by unstable molecules called free radicals.
Consuming leafy green vegetables may help reduce inflammation. The antioxidants in these vegetables may support overall health and reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases.
Green vegetables contain compounds that can act as prebiotics. These nutrients feed beneficial bacteria in your gut, which may support digestion and immune function. The plant compounds in green juice may also support digestive health by promoting a diverse mix of helpful bacteria.
However, juicing removes most of the fiber from vegetables, which is essential for digestive health. Eating whole vegetables provides more fiber. Experts suggest that half of your daily fruit intake should come from whole fruit.
Enjoying a glass of vegetable juice before meals may benefit your blood sugar levels. Stable blood sugar is crucial for your energy levels and long-term health.
A 2019 study found that drinking vegetable juice 30 minutes before eating led to more gradual increases in blood glucose compared to not drinking juice before the meal. The vegetable juice in the study was a commercial blend containing multiple vegetables, not specifically green juice. However, the findings suggest that vegetable-based juices may support blood sugar management.
When choosing a store-bought green juice, scan the label first. The ingredients appear in descending order by weight, so vegetables should be listed first. Also, check the nutrition label for added sugars. Green juice made from whole vegetables, without added sweeteners, should have zero grams of added sugars.
You’ll get more nutrients from fresh-pressed or homemade green juice than from heat-processed versions. Research shows that pasteurization can reduce vitamin C content and other heat-sensitive nutrients in juices. So, opting for fresh juices gives you the most benefits.