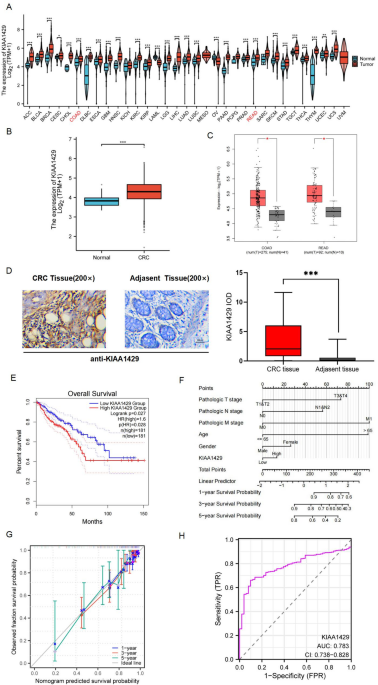
Integrated analysis of KIAA1429 expression patterns, clinical significance, and function by databases
KIAA1429 expression profiles in CRC, and pan-CRC cohorts were systematically analyzed using TCGA transcriptomic data and GEPIA 2.0 validation. Visualization was performed through ggplot2, stats, and car packages in R (v4.2.1). PD-L1 co-expression were assessed via cBioPortal database.
Clinical prognostic evaluation incorporated Kaplan-Meier survival curves (GEPIA 2.0) and Cox regression-based nomogram construction (survival/rms packages), integrating pathological staging (TNM), age, gender, and KIAA1429(Also Known As VIRMA) expression levels. Diagnostic performance was quantified through ROC curve analysis (pROC package).
Functional characterization involved: (1) PPI network construction using STRING database (Cytoscape v3.7.1); (2) Pathway enrichment analysis via KEGG/GO annotations (MSigDB reference genes, FDR < 0.05 threshold)37,38,39.
Multi-dimensional immune infiltration profiling through CIBERSORT algorithm implementation (ggalluvial/ggplot2 visualization modules). Initially, we performed a preliminary screening by investigating the correlation between molecules and immune cell infiltration. We then delved deeper into the relationship between molecular expression levels and immune cell infiltration to elucidate the mechanistic link between KIAA1429 expression and immune cell dynamics. Furthermore, we validated the aforementioned results in COAD and READ via the TCGA database.
Methodological unification included standardized R package workflows (v4.2.1) for statistical computing and data visualization across all analytical phases.
Cell lines preparation
The human CRC-derived cell lines SW620, HCT8, HCT116, HT29, and the murine-derived CRC cell lines MC38 and CT26 were obtained from Shanghai Wen Ye Biotechnology Co. (Catalog numbers: MXC370, MXC153, MXC151, MXC183, MXC1130, MXC112). The cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium (10–040-CV, Corning) or DMEM medium (10–013-CV, Corning) with 10% fetal bovine serum (Sh30084.03, Hyclone) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (C0222, Beyotime). Cultures were maintained at 37 °C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. These conditions ensured optimal cell viability and proliferation throughout the study.
Clinical samples acquisition
A total of 53 postoperative tumor tissue samples and 33 adjacent normal tissue samples were collected from CRC patients who underwent radical surgery at Taizhou People’s Hospital, affiliated with Nanjing Medical University, between 2020 and 2022. Clinicopathological data were gathered for all participants. (Patients inclusion criteria: Patients diagnosed with CRC through histopathological examination, Patients who underwent radical surgery for CRC at the hospital and No restrictions on age or gender. Patients exclusion criteria: Patients who had received prior anti-tumor treatments before surgery, Incomplete clinical records, Concurrent diagnosis of other malignancies, Presence of other severe systemic diseases.
The tissue specimens involved in this study were obtained from the Department of Pathology, Taizhou People’s Hospital, Nanjing Medical University. Clinical staging was referred to the American Joint Committee of Cancer (AJCC)/Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) TNM staging criteria for colorectal cancer (8th edition, 2017). The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Taizhou People’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. Informed consent was waived by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Taizhou People’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University (Approval Number: KY-2023-152-01), and all methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Animals
4–6 weeks of BALB/c, C57BL/6 female mice each 20 mice, each weighing 18 ± 2 g, each kind of mice were randomly divided into 4 groups, each group of 5 mice, The mice were housed under specific pathogen-free (SPF) conditions in a temperature-controlled environment at 25 °C, with a 12-hour light-dark cycle and ad libitum access to food and water. Mice subcutaneously injected CT26 and MC38 cells with or without KIAA1429 knockdown by siRNA. And the silencing effect was ensured by regular and quantitative intratumoral injection of the corresponding siRNA. Specifically, Injection of the corresponding siRNA was initiated at the same site (subcutaneously/intratumorally) 2 to 3 days after cell inoculation into the mice, with a frequency of twice a week. When the subcutaneous tumors grew to a size of 50–100 mm³, a group of mice of each species was randomly selected to receive intraperitoneal injections of anti-PD1(BioXCell, BE0146) twice a week. The specific groups and treatments are detailed in Table 1. Treatments were administered for 2–3 weeks. Tumor size and mouse body weight were recorded every three days, and tumor growth curves were plotted. At the end of treatment or when the tumor volume of mice ≥ 2000 mm3 the mice were executed by cervical dislocation method under Isoflurane (R510-22-10, RWD Life Science) inhalation anesthesia, and the subcutaneous tumor tissues were stripped and removed, and the weights were measured and photographed for recording.
The methods used to create animal models and dosage of drugs used refer to previous literature40,41. The animal study protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Collaborating Laboratory of Taizhou People’s Hospital affiliated with Nanjing Medical University (Approval Number: HJSW-24120101). All methods were conducted according to relevant guidelines and regulations which are reported under the ARRIVE guidelines.
Table 1 8 groups of mice treated (n = 5).Immunohistochemistry
Paraffin-embedded tissue specimens were sectioned into 4 μm slices. The water bath temperature was maintained at 45–50 °C, followed by natural flattening and baking in a thermostatic oven at 40 °C for 0.5–2 h. Deparaffinization and rehydration were carried out using 100% xylene and gradient ethanol. Endogenous peroxidase activity was sealed with 0.3% hydrogen peroxide for 15 min, followed by antigen repair. After blocking non-specific binding, the membrane was sealed with 5% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) for 30 min. Afterwards, primary antibodies, including KIAA1429 (25712-1-AP, Proteintech), PD-L1 (28076-1-AP, Proteintech), and CD8 (66868-1-IG, Proteintech), were applied and incubated overnight at 4 °C. After overnight incubation at 4 °C, the secondary antibodies were incubated for 30 min at room temperature. Immunostaining was visualized using the Envision System with diaminobenzidine as the chromogen. The result of CD8+T cell was evaluated by selecting three microscopic fields with the highest lymphocyte positivity. Quantitative analysis using Image Pro Plus 6.0 software determined the positive cell count, which was converted to cell density. The average density from the three fields was used for statistical evaluation. The result of KIAA1429 and PD-L1 was performed as follows: For each tissue section, three distinct microscopic fields were selected. For PD-L1, these fields were specifically chosen from areas showing positive expression. Using Image Pro Plus 6.0 software, the positive area and mean optical density were measured for each selected field. The integral optical density (IOD) was calculated by multiplying these two parameters, and the average IOD across the three fields was determined. This average served as the statistical indicator. Based on the median value of this indicator, samples were categorized into high – and low – expression groups.
Western blot
Add the sample buffer to the protein sample, adjust the final concentration of total protein to 1 mg/ml, boil the sample solution in boiling water at 100℃ for 5 min, put it on ice and centrifuge it at 3000 rpm/min for 1 min. 20 µl of sample solution was added to each well, and 10 µl of pre-stained marker was added to each well. 70v constant voltage electrophoresis was used for about 30 min, and the indicator bromophenol blue entered into the separator gel after it was changed to 90v constant voltage electrophoresis. Switch to 90v constant voltage electrophoresis, turn off the power when the indicator reaches about 0.5 cm from the lower end of the gel, and remove the gel plate. Configure the membrane transfer solution using Glycine (K41808066121, GE), Tris (2A210306310, Geneview) and methanol (10014118, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co.). After transferring the proteins in the gel to the PVDF membrane (ISEQ00010, Millipore) by the membrane transfer solution, the membrane was placed in 5% BSA closed at room temperature for 2 h, and then placed in the configured primary antibody solution β-actin (D191047, BBI), and at 4 °C overnight. The membrane was incubated with secondary antibody (D110087, BBI) for 2 h at room temperature. Protein bands were visualized with an enhanced chemiluminescence system. Antibodies were eluted using antibody stripping solution (SB-WB007z, share-bio) and then closed again for 2 h. Re-incubate the primary antibody PD-L1 (17952-1-AP, Proteintech), and secondary antibody (D110058, BBI) sequentially. Protein bands were visualized with an enhanced chemiluminescence system and quantified using Image J software, and each sample was tested 3 times.
qRT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent (9108, TAKARA), and the RNA content was detected using a spectrophotometer (NanoDrop 2000, Thermo Scientific). RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA by reverse transcription kit, and then quantitative polymerase chain reaction was performed by SYBR Premix Ex Taq (20ul reaction system configuration: SYBR Premix Ex Taq 10 µl, cDNA 2 µl, forward primer (10 µM) 1 µl, reverse primer (10µM) 1 µl, and 6 µl of sterilized distilled water). Program steps: pre-denaturation: 95 ℃, 5 min, 1 cycle; PCR reaction: 95 ℃ 15 s, 60 ℃ 30 s, 40 cycles; extension reaction: 60 ℃ 2 min, 1 cycle). The relative mRNA levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method with GAPDH as the internal reference gene, and each sample was tested 3 times. Primer sequences are available at Table 2.
Table 2 Primer sequences for qPCR.Flow cytometry
Tumor tissues were cut into fine pieces with ophthalmic surgical scissors. Add collagenase to digest at 37℃ for 10–30 min, remove the tissue pieces with a 200-mesh sieve, and collect the eluate. Add 1 ml of erythrocyte lysate separately, incubate at 4 °C for 10 min, centrifuge, 1200 rpm for 5 min. Discard the supernatant and shake. Add 2 ml of PBS wash solution, shake, centrifuge, 1200 rpm, 5 min. Add the corresponding antibody to each tube (CD3-FITC: 100204; Biolegend, CD4-PECY7: 100528; Biolegend, CD8-APC: 100712; Biolegend, CD45-pecy5: 103110; Biolegend) 5ul/each. Shake each tube after addition of antibody and keep away from light for 20 min at room temperature. Centrifuge and discard the supernatant, and shake. PBS 500 µl was added and the cell content was detected by flow cytometry (EXFLOW206; DAKEWE). Data analysis was performed with Flow Jo software (Version 10.8.1).
Immunofluorescence
Tumor tissues were dehydrated using gradient ethanol, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned into 4 μm slices. Sections were flattened in a 45–50 °C water bath, dried at room temperature, and baked at 40 °C for 0.5–2 h. The slices were deparaffinized using xylene and gradient alcohol and then rehydrated. After antigen repair using citric acid (PH6.0) antigen repair solution (G1202, Servicebio) the sections were closed with 5% BSA (G5001, Servicebio)/0.01mPBS (G0002, Servicebio) for 30 min. Primary antibodies, including CD3(17617-1-AP, Proteintech), CD8(66868-1-IG, Proteintech) were placed in the refrigerator at 4 °C overnight. and the next day it was left at room temperature for 15 min to rewarm, and fluorescent secondary antibody was added dropwise (FITC, D110061- 0100, BBI; CY3: D110088-0100, BBI), and incubate at room temperature for 30 min avoiding light. PBS washed for 5 min×5 times, PBS outside the specimen was wiped off with filter paper, and incubated for 2 min avoiding light by adding drops of DAPI. The specimen was washed with PBS for 1 min×3 times to remove the DAPI. Finally, the plate was sealed with glycerol and observed under the microscope immediately.
Statistical methods
The statistical analyses of the results generated by online interactive web servers using public databases [GEPIA2 database (http://gepia2.cancer-pku.cn), TIMER2.0 database (http://timer.cistrome.org), cBioPortal database (https://www.cbioportal.org), and SRAMP database (http://www.cuilab.cn/sramp)]. The results generated were calculated automatically. These results were considered statistically significant at *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. The rest of the experimental results were plotted using Graphpad Prism 10 software for data analysis. The chi-square test was used for comparison of the count data and was considered statistically significant at P < 0.05. T-test and two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used for comparison of measurement data, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant, and bar charts and scatter plots were plotted. Correlation analysis was performed using Spearman’s correlation analysis, and scatter plots were drawn.