Kirin Holdings is working to launch R&D facilities across the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region to reach global scale and address local needs. To start, it will establish a new company, Kirin Health Science International, in Australia this April, which will unify business activities under a global brand strategy and standardized business processes.
Additionally, Kirin focuses on boosting research in fermentation technology and biotechnology to power product and business development.
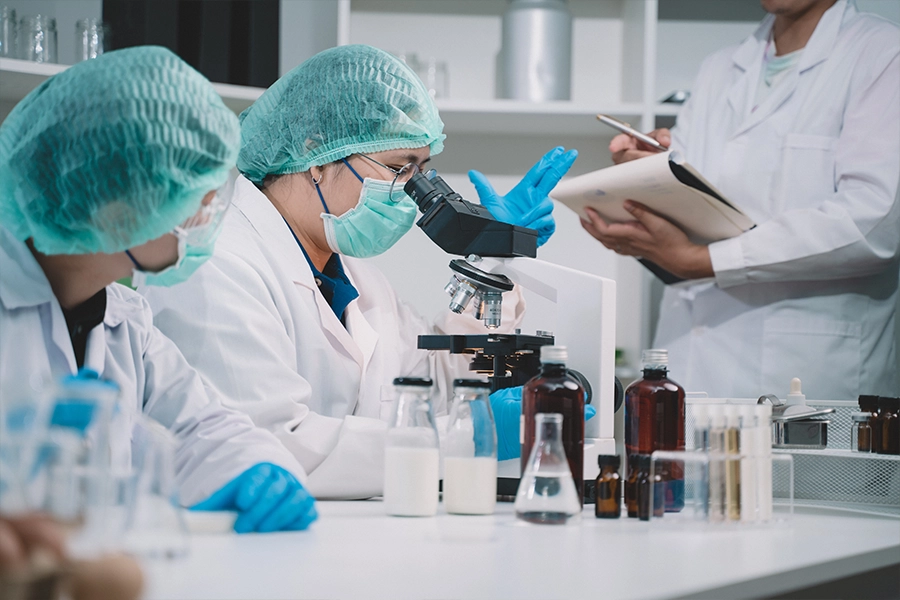
The company states that it will increase R&D investment to approximately 1.5 times (150%) the 2025 level by 2035. The first phase will take ¥3.5 billion (US$22.8 million) for research facilities at the Institute for Technology of Microbial Science this year.
For immune health supplements, the company is expanding its Lactococcus lactis Plasma (LC-Plasma) postbiotic into high-growth markets, with particular focus on APAC. It has been conducting two clinical trials in Australia to deepen its understanding of LC-Plasma’s mechanism of action.
LC-Plasma is a heat-killed lactic acid bacterium with over 34 studies backing it as an immunity booster. We previously spoke with the company about its first hot drink launch featuring LC-Plasma to support immune function. The postbiotic activates plasmacytoid dendritic cells, known as the “command centers of the immune system,” in humans, helping maintain immune function in healthy individuals.
Furthermore, in Japan, the company is working to raise awareness of immunity care, aiming to partner with municipalities, workplaces, kindergartens, and learning centers to foster healthy habits in the public.
Nutrition Insight meets with a spokesperson at the company’s R&D Division at the Institute of Health Science to learn about its approach and investment in R&D.
Kirin plans to significantly expand R&D spending by 2035. Which health questions are worth a long-term investment?
Institute of Health Science: Our most important decision criterion is whether a given area can generate both long-term social value and business value. We base our investment decisions on three considerations:
Whether the area has a strong scientific foundation and allows us to contribute through our unique expertise.Whether sustainable market growth can be expected in addressing future social issues.Whether we can anticipate contributions to earnings-per-share growth and ensure capital efficiency.
Immune care is a major focus at Kirin, but immunity is influenced by many factors. Do you believe food and fermentation are important?
Institute of Health Science: Food and fermentation support immunity by building the foundation for everyday immune care. They are not expected to treat diseases in the way pharmaceuticals do. However, by combining continuity and safety with multilayered physiological functions and scientifically validated functionalities, we believe this field offers realistic and highly meaningful social value.
 Tomoya Tomago, Ingredient brand manager at Kirin, discussed LC-Plasma’s 20% growth year-over-year and Japanese immunity market trends.Recent research has shown that fermentation is being reevaluated not merely as a traditional preservation technique or a process to enhance nutritional value, but as a platform for generating bioactive functions. In the process, diverse metabolites produced by microorganisms can contribute to health benefits.
Tomoya Tomago, Ingredient brand manager at Kirin, discussed LC-Plasma’s 20% growth year-over-year and Japanese immunity market trends.Recent research has shown that fermentation is being reevaluated not merely as a traditional preservation technique or a process to enhance nutritional value, but as a platform for generating bioactive functions. In the process, diverse metabolites produced by microorganisms can contribute to health benefits.
While the functionality of fermented foods was traditionally assumed to derive from known components, advances in analytical technologies have revealed that newly generated, previously uncharacterized metabolites are produced through microbial fermentation. These may influence physiological functions such as immunity and inflammation.
We have confirmed that the fermentation process can serve as a source for discovering functional ingredients. There is a growing movement to reconceptualize fermentation not as an extension of tradition but as a scientifically designable foundation for health science. As a result, assumptions surrounding fermentation are shifting from a static view of food processing to a dynamic and application-oriented biotechnology with far-reaching potential.
As you explore novel health solutions, how do you balance promising early findings with evidence?
Institute of Health Science: We do not judge the future potential of next-generation health solutions based solely on promising early results. Instead, we place the highest priority on ensuring both scientific validity and reproducibility that can withstand everyday use. In the initial stages, a clearly defined mechanistic hypothesis and confirmation of safety are mandatory. We then accumulate data step by step across diverse populations that differ in age, living environment, and modes of intake.
 Kirin is expanding biotechnology and fermentation R&D across APAC, with immune care at the core focus through 2035.Furthermore, with practical implementation of food ingredients in mind, we verify long-term effects under real-life conditions and assess suitability in forms that users can easily consume. By progressively integrating the scientific potential identified in early research with the universal evidence required for social implementation, we avoid overgeneralization and ensure that only health benefits supported by robust evidence reach the market.
Kirin is expanding biotechnology and fermentation R&D across APAC, with immune care at the core focus through 2035.Furthermore, with practical implementation of food ingredients in mind, we verify long-term effects under real-life conditions and assess suitability in forms that users can easily consume. By progressively integrating the scientific potential identified in early research with the universal evidence required for social implementation, we avoid overgeneralization and ensure that only health benefits supported by robust evidence reach the market.
Sustainability and health are increasingly linked. How does this connection shape the way you design research?
Institute of Health Science: We adopt a policy of embedding sustainability not as an outcome of product development but as an integral part of the research and design process. For example, we are considering defining research themes in areas where biotechnology, particularly fermentation, can be leveraged to create high functional value through processes with low environmental impact.
In addition, our approach to diverse health challenges focuses on enhancing the body’s inherent capabilities, using this as an evaluation criterion to determine whether solutions can lead to long-term outcomes without relying on pharmaceutical interventions. Furthermore, in clinical research, we verify applicability across groups with different ages and living environments and assess the feasibility of social implementation by examining continuity of everyday use.
Through this design philosophy, we place strong emphasis on achieving sustainability and health value from the earliest stages of research.