What are antibodies? Antigens vs Antibodies. What are antibodies and it’s types?
creative medical studio.
what is antibodies in Urdu
what do antibodies do
what are antigen and antibodies
what is antigen presenting cells
what is antigen antibodies reactions
Antibodies are proteins that protect you when an unwanted substance enters your body. Produced by your immune system, antibodies bind to these unwanted substances in order to eliminate them from your system.
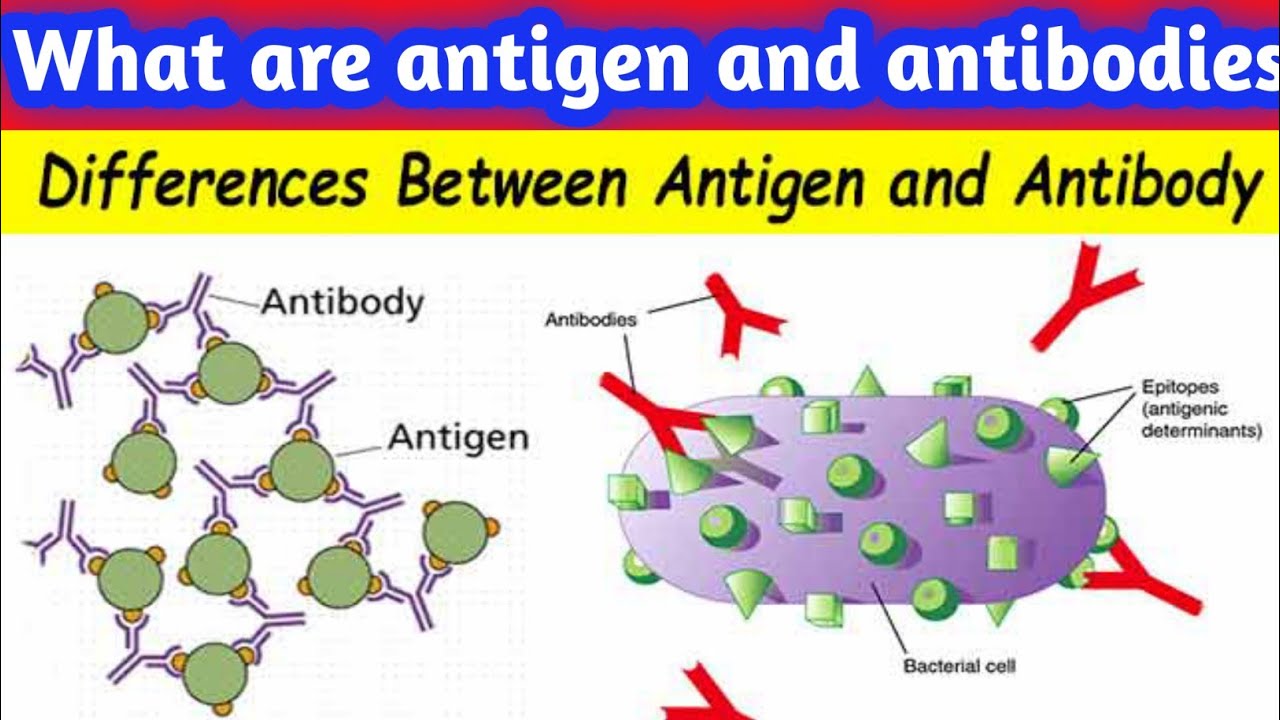
Antigen vs antibody
An antigen is a foreign substance that enters your body. This can include bacteria, viruses, fungi, allergens, venom and other various toxins. An antibody is a protein produced by your immune system to attack and fight off these antigens.
How do antibodies fight off antigens?
The molecules on the surfaces of antigens differ from those found naturally in your body. So, when an antigen enters your body, your immune system recognizes it right away. In order to attack this antigen invader, your immune system calls out for antibody protection.
Where are antibodies produced?
Antibodies are produced by B cells (specialized white blood cells). When an antigen comes into contact with a B cell, it causes the B cell to divide and clone. These cloned B cells — or plasma cells — release millions of antibodies into your bloodstream and lymph system.
Antibodies are located in various areas of your body, including your skin, lungs, tears, saliva and even breast milk. In fact, high amounts of antibodies are present in colostrum (a thick fluid secreted by the breasts for a few days after giving birth). That’s why breastfeeding can boost your baby’s immune system.
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies are created in a lab. They mimic your immune system’s natural ability to fight off pathogens. Using monoclonal antibodies to fight infections is a type of immunotherapy.
Function
What are the 5 types of antibodies and their function?
Antibodies are categorized into five classes according to their location. Each one is labeled by a letter, which is attached to an abbreviation of the term “immunoglobulin” (Ig):
IgA; Found in saliva, tears, mucus, breast milk and intestinal fluid, IgA protects against ingested and inhaled pathogens.
IgD; This antibody is found on the surface of your B cells. Though its exact function is unclear, experts think that IgD supports B cell maturation and activation.
IgE; Found mainly in your skin, lungs and mucus membranes, IgE antibodies cause your mast cells (a type of white blood cell) to release histamine and other chemicals into your bloodstream. IgE antibodies can cause allergic reactions.
IgG; This is the most common antibody, making up approximately 70% to 75% of all immunoglobulins in your body. It’s found mainly in blood and tissue fluids. IgG antibodies help protect your body from viral and bacterial infections.
IgM; Found in your blood and lymph system, IgM antibodies act as the first line of defense against infections. They also play a large role in immune regulation.
What are antibodies made of?
Antibodies are proteins. Each antibody has four polypeptides (peptides that consist of two or more amino acids), including two heavy chains and two light chains.
What do antibodies look like?
Each antibody structure consists of two heavy chains and two light chains, which join to form a Y-shaped molecule. Each type of antibody has a different amino acid sequence at the tips of the “Y” which is why each antibody is shaped differently.
#medical #ultrasound #medicaleducation #hospital #medicallectures #antibiotics #antigen #antibodies #antibody #infection #inflammation #whitebloodcells #wbcs