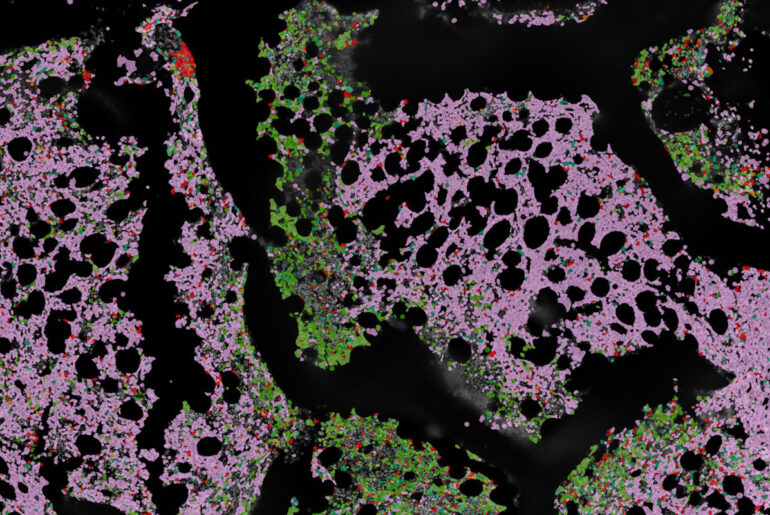
Pain-sensing gut neurons don’t just detect discomfort — they help launch allergic immune reactions, according to a new study from Weill Cornell Medicine. Researchers found these neurons can kick-start inflammation tied to asthma and allergies, a discovery published in Nature.
The team showed that when pain-sensing neurons activate, they signal specialized gut cells called tuft cells to rapidly multiply and release immune molecules. In mouse experiments, this response helped fight parasites but also triggered the same type of inflammation seen in allergic disease.
Silencing those neurons weakened the immune response, while activating them caused tuft cell numbers to surge within 24 hours. The findings suggest today’s allergy and asthma drugs may fall short because they ignore the nervous system’s role.
Researchers say future treatments could work better by targeting both nerves and immune cells.
Get the latest local headlines every morning at 6 a.m. Sign up for our Get Local newsletter .
Want to see more FingerLakes1.com stories in Google? Add FingerLakes1.com to your preferred news sources to help Google prioritize our reporting in your results.
FingerLakes1.com is the region’s leading all-digital news publication. The company was founded in 1998 and has been keeping residents informed for more than two decades. Have a lead? Send it to [email protected].